Narrowband IoT is a low power wide area network technology developed by 3GPP to enable cellular devices and services. Also, NB-IoT is known as LTE cat NB1. It’s classified as 5G technology and standard by 3GPP. NB-IoT can connect a large number of devices and the number is up to 50,000 per NB-IoT network cell. NB-IoT features meet many challenges. NB-IoT can connect many devices to the internet of things and create many new applications. It can be optimized for applications that need a small amount of data for a long period of time. The existing cellular network does not support power-saving mode, whereas the NB-IoT network runs on low power.
NB-IoT network is available in many countries. It is available in Austria, Thailand, Portugal, United States, Belgium, China, UAE, Ukraine, and many more. Due to its low cost and longest battery life and other advantages, it is used as one of the best available networks in the market. There are different advantages like low power consumption, easy to establish in an existing cellular network; it uses guard band, a large number of devices connected at one time and many more, because of these biggest advantages it is at boom stage in the many countries.
However, there are many applications of this network that likes smart cities, smart home, agriculture, healthcare, use for a smart tracking device, manufacturing and logistics, and many more. This could be achieved because of NB-IoT’s technical advantage. To understand how it is possible, we have to understand its technical details. Let’s have look at its network architecture and technical features.
➥NB-IoT Network Architecture: Here, NB-IoT network architecture is shown for getting an overview.
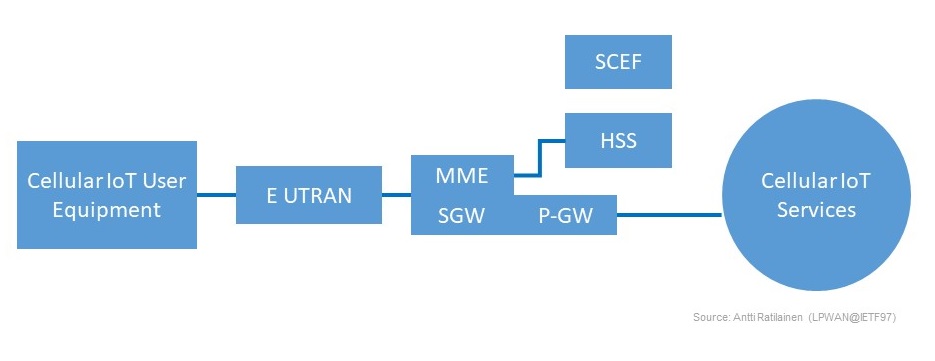
This is the one of network architecture which is Evolved packet core architecture with cellular IoT. SCEF: Service capability Exposure Function; PGW: Packet Data Node Gateway; S-GW: Serving Gateway; HSS: Home Subscriber Server; MME: Mobility Management Entity.
Cellular IoT user equipment used to connect IoT devices instead of creating a new and private network. Cellular IoT offers an alternative low power, wide area networks that operate in unlicensed bands. The E-UTRAN is an air-interface of 3GPP long term evolution way for mobile networks. The E-UTRAN used for radio communications between the device and the evolved packet core.
The mobility management entity is playing an important role in EPC architecture. The mobility management entity is the main signalling node in the EPC. The main function of the serving gateway is the routing and forwarding of user data packets. Also, it is responsible for providing mobility between LTE and other networks. The PGW is responsible for interfacing between the LTE network and other packet data networks.
The function of HSS is to communicate with the network and provide subscriber profiles and authentication info. The database stores info of subscriber and help in authorization and details of the device. The SCEF is a product deployed in a policy management network that interacts with the internet of things devices as a machine type communication interworking.
As described functions of each entity, the communication happens in this way in the NB-IoT network. These are the basic technical details of the network architecture of NB-IoT.
➥NB-IoT basic technical features: The extended coverage of NB-IoT is 20 dB better than GPRS. The extended coverage of NB-IoT is 164 dB MCL (Maximum coupling loss). GPRS has a 3% outage for the indoor area with 20 dB penetration loss because of the low MCL of 144 dB. There is a different range for the different network for connecting the devices. We can connect about 40 devices per household with NB-IoT. Uplink report latency is less than 10 seconds.
Technical Characteristics: It is easy to implement the NB-IoT network in the existing 3GPP network. There are three deployments modes in the M2M Nb-IoT network.
➥Stand-alone operation
➥Operation in LTE guard band
➥Operation within a wider LTE carrier
There are three protocols in NB-IoT which play a vital role in the communication of the network. These are L1, L2 and L3 protocols.
➥L1 Protocol: In L1, there is FDD (Frequency division duplex) present and the half-duplex User equipment is there. Whereas, narrow-band physical downlink channels communication happen over 180KHZ. However, narrow-band physical uplink channel communication happens over 15 kHz or 3.75 kHz. If we look at the transport block size then the Maximum transport block size is in downlink is 680bits and 1000bits in an uplink.
➥L2 and L3 protocol: These protocols are important as L1. In these protocols, MTU (Maximum transmission unit) is 1500bytes. Also, these protocols support a multi-physical resource block. L2 supports both the Non-access stratum and access stratum. NAS is a protocol that is used to convey non-radio signalling between UE and network. NAS helps in authentication, security, and mobility system.
Access stratum is responsible for transporting data over wireless networks and helps to manage radio resources. The security of L2 and L3 is good enough to transmit data over these protocols. It helps to encrypt and integrating protection in both access stratum and non-access stratum.
NB-IoT has a vast range of applications; one certain application of NB-IoT is the Energy Monitoring system which is being developed at AumRaj Design Systems. It is developed to successfully overcome challenges like noisy industrial environment, uninterrupted bidirectional wireless communication between Node and Server in an industrial environment; moreover, it is assisted by a rechargeable battery with a week’s standby time. This system is developed in such a fashion that it is not restricted to Energy Monitoring, with calculated alteration it can also be used for smart security system with intruder alert, smart factories with an automated production line, smart metering of (electricity, gas, and water), Fleet Management, smart parking meters and much more. The rising demand for NB-IoT in the wireless sector is an indication that evolution is still on its way.



