Big complex systems, like power plants, ships, or fleets are consist of multiple systems, subsystems, and components built on different technologies like mechanical, electronic, electrical, and software. When they are working together as embedded systems operating as a fleet, with time, it raises maintenance issues and the life cycle of the whole system. In many cases, a fleet operation is optimized in terms of production, making system availability a day to day concern. So, Fleet Prognostics and Health Management (FPHM) play a pivotal role in controlling the performance and operating level of such a system. The FPHM system helps to prevent failure of the fleet and predict maintenance time of the fleet in advance.
Due to a large fleet, the fleet or plant operation is optimized manually. Because of manual optimization, the probability of failure increase. So, FPHM plays a key role to ensure system performance, in getting advanced acknowledgment or notification for maintenance strategies.
FPHM knowledge-based system on proactive fleet management hierarchy
The FPHM knowledge based on proactive fleet management hierarchy is developed on the knowledge-intensive process. To support the main FPHM process development and to achieve a better result of monitored data, for diagnostic and maintenance decision making, the below domain knowledge needs to be required. The system should enable:
➥Manage condition monitoring activities
➥Link associate monitored data with component operating condition
➥Compare the diagnostic process with FPHM facilities
➥Signal of pro-actively anticipate failure
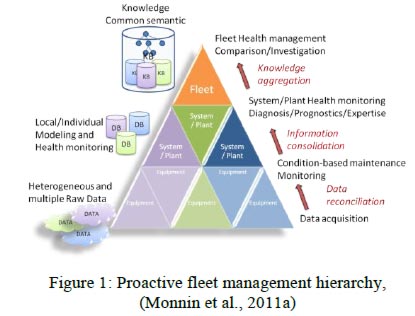
This will ensure consistent information to be used throughout the process, from raw data acquisition to FPHM comparison. The main factor to turn data into such information is to enhance data with semantic context by means of ontology.
Knowledge domain modeling depends on the formal language that allows concepts to be described as well as the relationships that hold between these concepts. As starting from basic concepts, complex concepts can therefore be built up in definitions out of simple concepts. A recent development in the semantic modeling, based on information used and its concepts, have to lead techniques using ontology to model complex system. The physical relationships between physical components stores in the ontology as well as more abstract concepts about the components and their usage stored in an ontology.
FPHM expertise recuperation
For diagnostic comparison, contextual information from the ontology enables to group components together given a particular context. The four levels of context are defined in order to offer comparison facilities:
➥Technical context
➥Service context
➥Operational context
➥Performance context
The technical context allows the technical features of the components to be described in the ontology. The technical context describes all the technical features of the system. From the practical point of view, the operating context can influence the component behavior.
The service context deals with sub-system with components, even if they are similar, they undergo different solicitations. Even, if the components belong to the same type, their functions are different. Besides, components that belong to different types can be compared in a way that they operate in the same service context.
The operational context defines the operating condition of the system. They provide contextual information according to the system operation.
The performance context plays a pivotal role in the fleet and it informs there is a need for optimization is required or not. The performance context enables large and global consideration to comparative assess the global health of the fleet.
In the FPHM system, using all these contexts, the abnormal behavior of the system can be early detected. The indicators like performance allow early diagnostic and enable failure anticipation leading to planning adapted maintenance actions. The FPHM system helps enable efficient predictive diagnosis and failure anticipation.
The system architecture of the FPHM system
The typical system architecture of the FPHM system mentioned. The system is consists of an ontology model, ontology facilities that are connected with JENA API, and this is connected with data storage and user management system. The data is coming from ships and plants through passing warehouse data collection and reach to data storage and user management system.
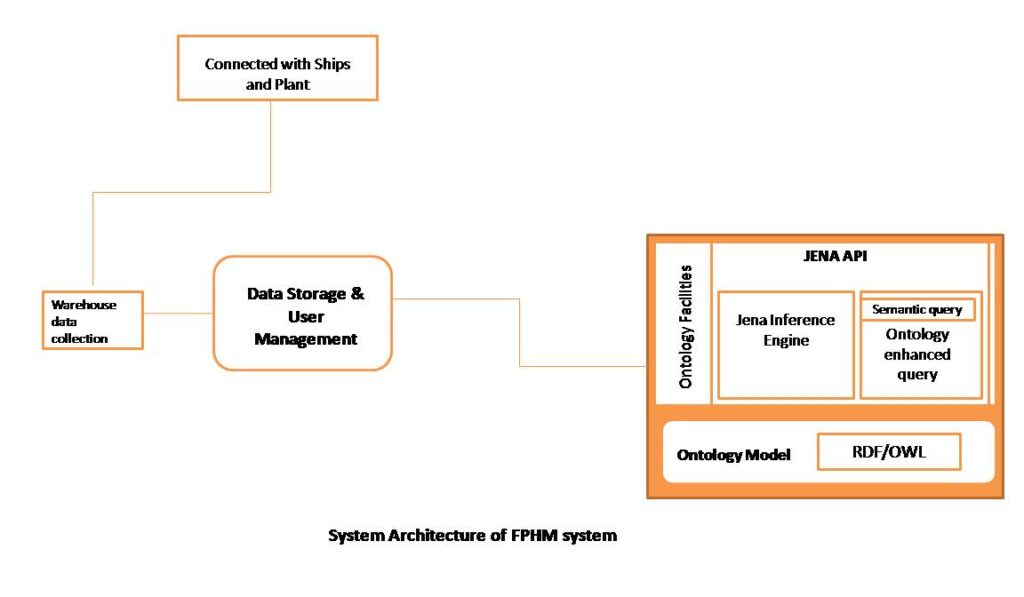
The ontology model is coded in ontology web language (OWL) that is the formal ontology language. The ontology can be divided into resource description framework (RDF) and OWL. The ontology model is integrated by SQL backed storage and the java framework JENA is used for ontology exploitation through data storage and user management module. This provides the user with a web portal that allows the benefiting of the FPHM. The JENA interface engine allows semantic queries to perform their task. Semantic queries allow for queries and analytics of associative and contextual nature. This is design to deliver precise results. Relevant contextual information can be retrieved and gathered for the purpose of failure anticipation, investigation.
The underlying monitoring data collected by the data warehouse. The platform integrates the ontology model on top of the warehouse data collection. The data can be available, on-line, off-line, or on-demand.
FPHM requires a knowledge-based system that is able to handle contextual information. Diagnosis and maintenance decisions can be simplified using FPHM system.



